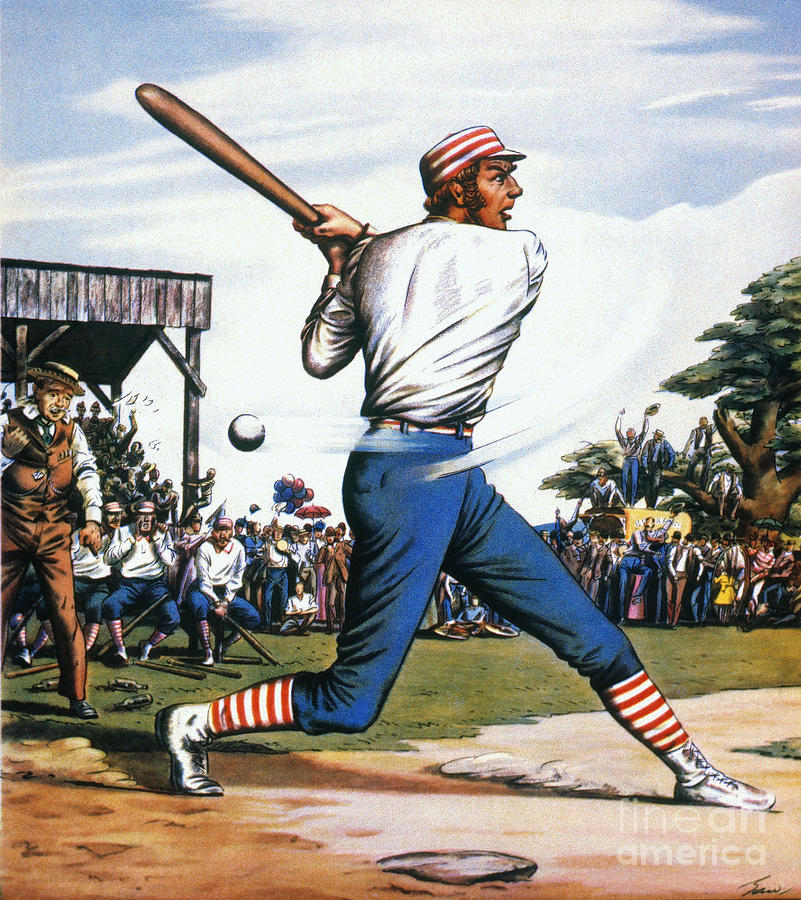
CASEY AT THE BAT
BY: Ernest Lawrence Thayer
A Ballad of the Republic, Sung in the Year 1888
The outlook wasn’t brilliant for the Mudville nine that day;
The score stood four to two with but one inning more to play.
And then when Cooney died at first, and Barrows did the same,
A sickly silence fell upon the patrons of the game.
A straggling few got up to go in deep despair. The rest
Clung to that hope which springs eternal in the human breast;
They thought if only Casey could but get a whack at that—
We’d put up even money now with Casey at the bat.
But Flynn preceded Casey, as did also Jimmy Blake,
And the former was a lulu and the latter was a cake;
So upon that stricken multitude grim melancholy sat,
For there seemed but little chance of Casey’s getting to the bat.
But Flynn let drive a single, to the wonderment of all,
And Blake, the much despised, tore the cover off the ball;
And when the dust had lifted, and men saw what had occurred,
There was Jimmy safe at second and Flynn a-hugging third.
Then from 5,000 throats and more there rose a lusty yell;
It rumbled through the valley, it rattled in the dell;
It knocked upon the mountain and recoiled upon the flat,
For Casey, mighty Casey, was advancing to the bat.
There was ease in Casey’s manner as he stepped into his place;
There was pride in Casey’s bearing and a smile on Casey’s face.
And when, responding to the cheers, he lightly doffed his hat,
No stranger in the crowd could doubt ’twas Casey at the bat.
Ten thousand eyes were on him as he rubbed his hands with dirt;
Five thousand tongues applauded when he wiped them on his shirt.
Then while the writhing pitcher ground the ball into his hip,
Defiance gleamed in Casey’s eye, a sneer curled Casey’s lip.
And now the leather-covered sphere came hurtling through the air,
And Casey stood a-watching it in haughty grandeur there.
Close by the sturdy batsman the ball unheeded sped—
“That ain’t my style,” said Casey. “Strike one,” the umpire said.
From the benches, black with people, there went up a muffled roar,
Like the beating of the storm-waves on a stern and distant shore.
“Kill him! Kill the umpire!” shouted some one on the stand;
And it’s likely they’d have killed him had not Casey raised his hand.
With a smile of Christian charity great Casey’s visage shone;
He stilled the rising tumult; he bade the game go on;
He signaled to the pitcher, and once more the spheroid flew;
But Casey still ignored it, and the umpire said, “Strike two.”
“Fraud!” cried the maddened thousands, and echo answered fraud;
But one scornful look from Casey and the audience was awed.
They saw his face grow stern and cold, they saw his muscles strain,
And they knew that Casey wouldn’t let that ball go by again.
The sneer is gone from Casey’s lip, his teeth are clinched in hate;
He pounds with cruel violence his bat upon the plate.
And now the pitcher holds the ball, and now he lets it go,
And now the air is shattered by the force of Casey’s blow.
Oh, somewhere in this favored land the sun is shining bright;
The band is playing somewhere, and somewhere hearts are light,
And somewhere men are laughing, and somewhere children shout;
But there is no joy in Mudville—mighty Casey has struck out.
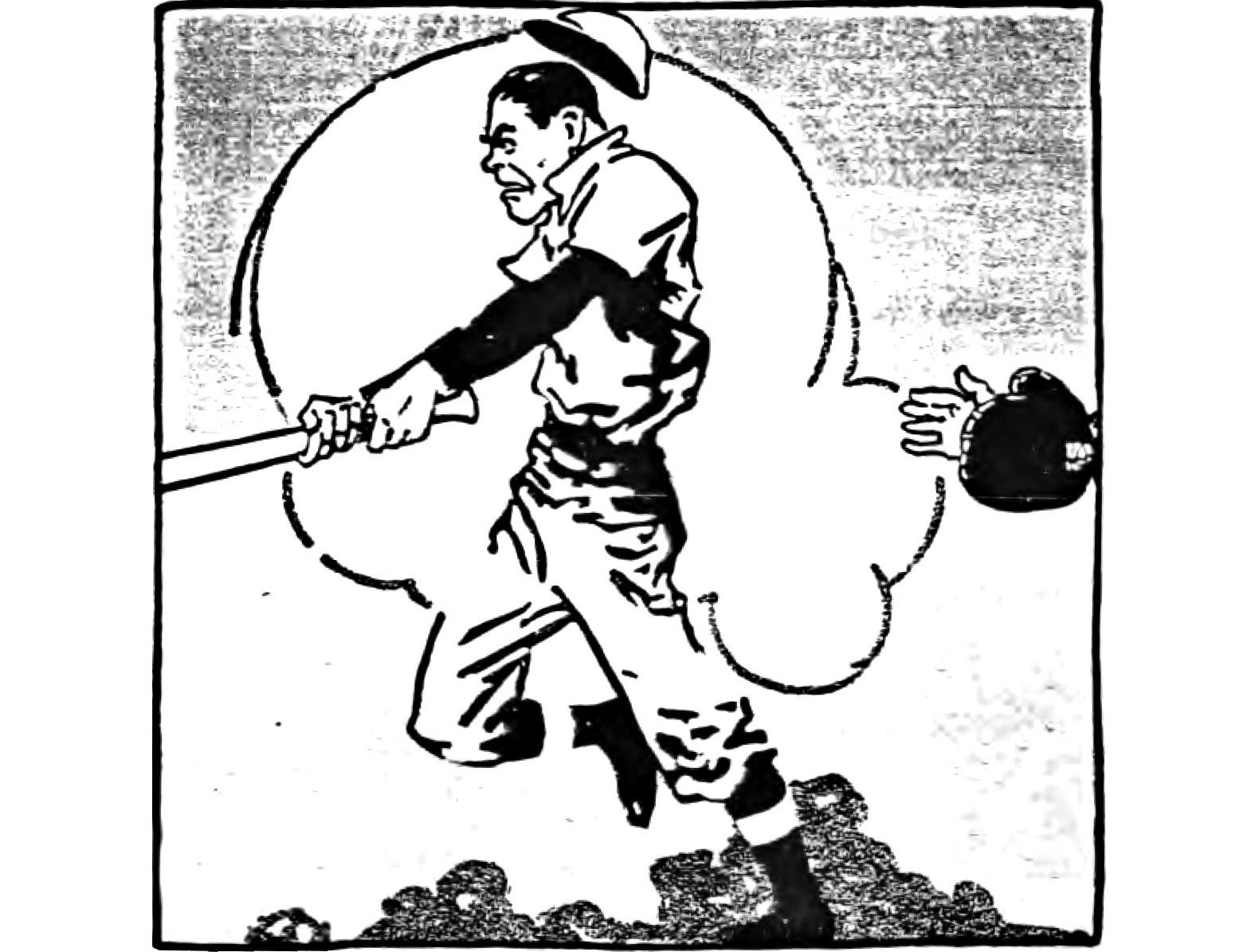

Do you even truly consider yourself American if you don’t know at least one stanza of this poem by heart? Unlike the mighty and fearless leader of Tavistock Books (and the San Francisco Giants’ #1 Fan) Vic Zoschak, I know relatively zilch about baseball. I know there are two teams, I know there are some innings, and I know the hot dogs are as delicious as they are terrible for you. So yeah, I basically know nothing about baseball. But Casey? Oh, I know all about that self-confident dud.
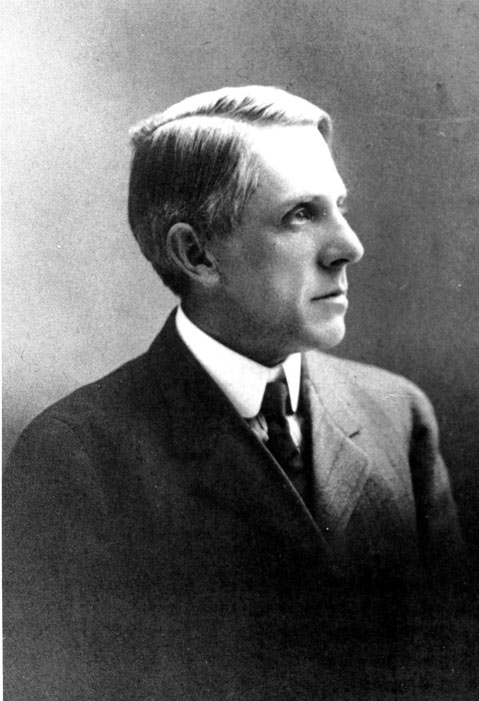 Ernest Thayer was a Harvard educated author, who began working at the age of 24 as a humor columnist for The San Francisco Examiner. On June 3rd, 1888, the elusive author “Phin” published a poem that would become a backbone of both American poetry and baseball. Thayer did not receive credit for the poem for several months (as he was not a boastful man), and when he finally did he was surprisingly close-lipped about it all. He never revealed whether he based the game or the character of Casey on a real player, though many have put forth possibilities.
Ernest Thayer was a Harvard educated author, who began working at the age of 24 as a humor columnist for The San Francisco Examiner. On June 3rd, 1888, the elusive author “Phin” published a poem that would become a backbone of both American poetry and baseball. Thayer did not receive credit for the poem for several months (as he was not a boastful man), and when he finally did he was surprisingly close-lipped about it all. He never revealed whether he based the game or the character of Casey on a real player, though many have put forth possibilities.
Actor William DeWolf Hopper was the first to read the poem aloud onstage – on August 14th, 1888 (Thayer’s birthday, as a matter of fact) at the Wallack Theatre in New York City. Present were the Chicago and New York baseball teams – the White Stockings and the Giants. Many of Hopper’s recitations of the poem can be heard today, as he became the official orator of the poem – and by the end of his life had recited it over 10,000 times. Thayer read it aloud just once, at a Harvard class reunion in 1895, which finally settled any doubts Americans had on the wordsmith and creator of the poem. Despite the fact that many knew of Thayer’s authorship, his lack of comment and humble nature had caused many to doubt it throughout the years!

Click here to listen to DeWolf Hopper reciting Casey at the Bat
Thayer lived in California for the bulk of his life working at the San Francisco Examiner, eventually moving in 1912 to Santa Barbara where he lived until he passed away at the age of 77.

Here is one of our many baseball offerings (we mentioned that Vic was a GIANT baseball fan, right? (See what I did there? That man loves the Giants.) Printed just two years prior to Thayer’s poem publication, this 125 page wrappered booklet claims to be the “Complete Hand Book of the National Game of Baseball.” Find out everything Thayer knew about the game here!
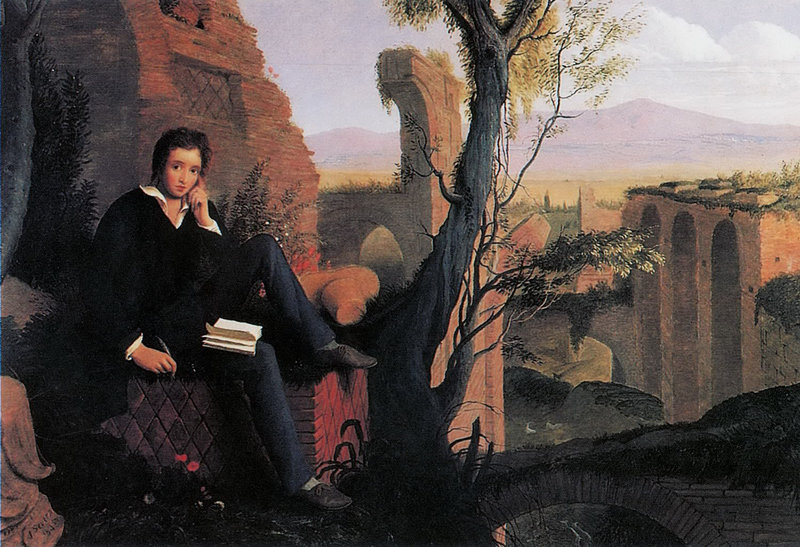









 In the summer of 1816, Shelley befriended one of his first powerful and influential authors – Lord Byron. Percy and Mary spent a season with Byron in Switzerland – the summer ended up being one of the most important of Shelley’s life. Byron helped inspire the young radical, and Shelley wrote his romantic poem Hymn to Intellectual Beauty after an afternoon with Byron. It was during this summer, funnily enough, that Byron’s guests and friends were inspired to have a horror write-off. This writing competition of sorts was the inspiration behind Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein. Upon their return to England at the end of the year, it was discovered that Shelley’s wife, Harriet, had committed suicide. As unfortunate as the event was, it incited Shelley and Mary to finally marry. The two settled in a small hamlet in Buckinghamshire, where they befriended poets John Keats and Leigh Hunt – both of which would prove to be invaluable friends to Shelley in his last years. It was in these years that Shelley wrote and published a bulk of his most well-known works, including The Revolt of Islam and Prometheus Unbound, the latter of which is widely considered to be his most beloved epic work.
In the summer of 1816, Shelley befriended one of his first powerful and influential authors – Lord Byron. Percy and Mary spent a season with Byron in Switzerland – the summer ended up being one of the most important of Shelley’s life. Byron helped inspire the young radical, and Shelley wrote his romantic poem Hymn to Intellectual Beauty after an afternoon with Byron. It was during this summer, funnily enough, that Byron’s guests and friends were inspired to have a horror write-off. This writing competition of sorts was the inspiration behind Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein. Upon their return to England at the end of the year, it was discovered that Shelley’s wife, Harriet, had committed suicide. As unfortunate as the event was, it incited Shelley and Mary to finally marry. The two settled in a small hamlet in Buckinghamshire, where they befriended poets John Keats and Leigh Hunt – both of which would prove to be invaluable friends to Shelley in his last years. It was in these years that Shelley wrote and published a bulk of his most well-known works, including The Revolt of Islam and Prometheus Unbound, the latter of which is widely considered to be his most beloved epic work.


 Ernest Thayer was a Harvard educated author, who began working at the age of 24 as a humor columnist for The San Francisco Examiner. On June 3rd, 1888, the elusive author “Phin” published a poem that would become a backbone of both American poetry and baseball. Thayer did not receive credit for the poem for several months (as he was not a boastful man), and when he finally did he was surprisingly close-lipped about it all. He never revealed whether he based the game or the character of Casey on a real player, though many have put forth possibilities.
Ernest Thayer was a Harvard educated author, who began working at the age of 24 as a humor columnist for The San Francisco Examiner. On June 3rd, 1888, the elusive author “Phin” published a poem that would become a backbone of both American poetry and baseball. Thayer did not receive credit for the poem for several months (as he was not a boastful man), and when he finally did he was surprisingly close-lipped about it all. He never revealed whether he based the game or the character of Casey on a real player, though many have put forth possibilities.


 So said the Little Prince – an absolutely beloved character in the canon of Western Literature. Antoine de Saint-Exupéry wrote this story, a children’s story on the outside and a very adult study of human nature and morality on the inside. Saint-Exupéry, a French national, had fled Europe at the onset of World War II and wrote much of his tale during his 27 week stay in North America and Canada. Now normally we would do a blog on Saint-Exupéry’s life story and how he came to write such a popular and precious children’s tale, but today we are speaking of a specific day in this author’s life… the day he disappeared from the skies.
So said the Little Prince – an absolutely beloved character in the canon of Western Literature. Antoine de Saint-Exupéry wrote this story, a children’s story on the outside and a very adult study of human nature and morality on the inside. Saint-Exupéry, a French national, had fled Europe at the onset of World War II and wrote much of his tale during his 27 week stay in North America and Canada. Now normally we would do a blog on Saint-Exupéry’s life story and how he came to write such a popular and precious children’s tale, but today we are speaking of a specific day in this author’s life… the day he disappeared from the skies.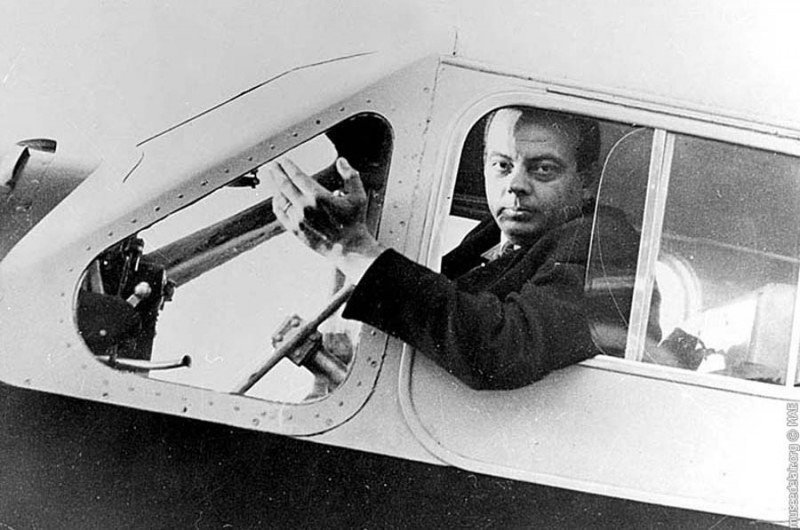
 Unfortunately,
Unfortunately, 
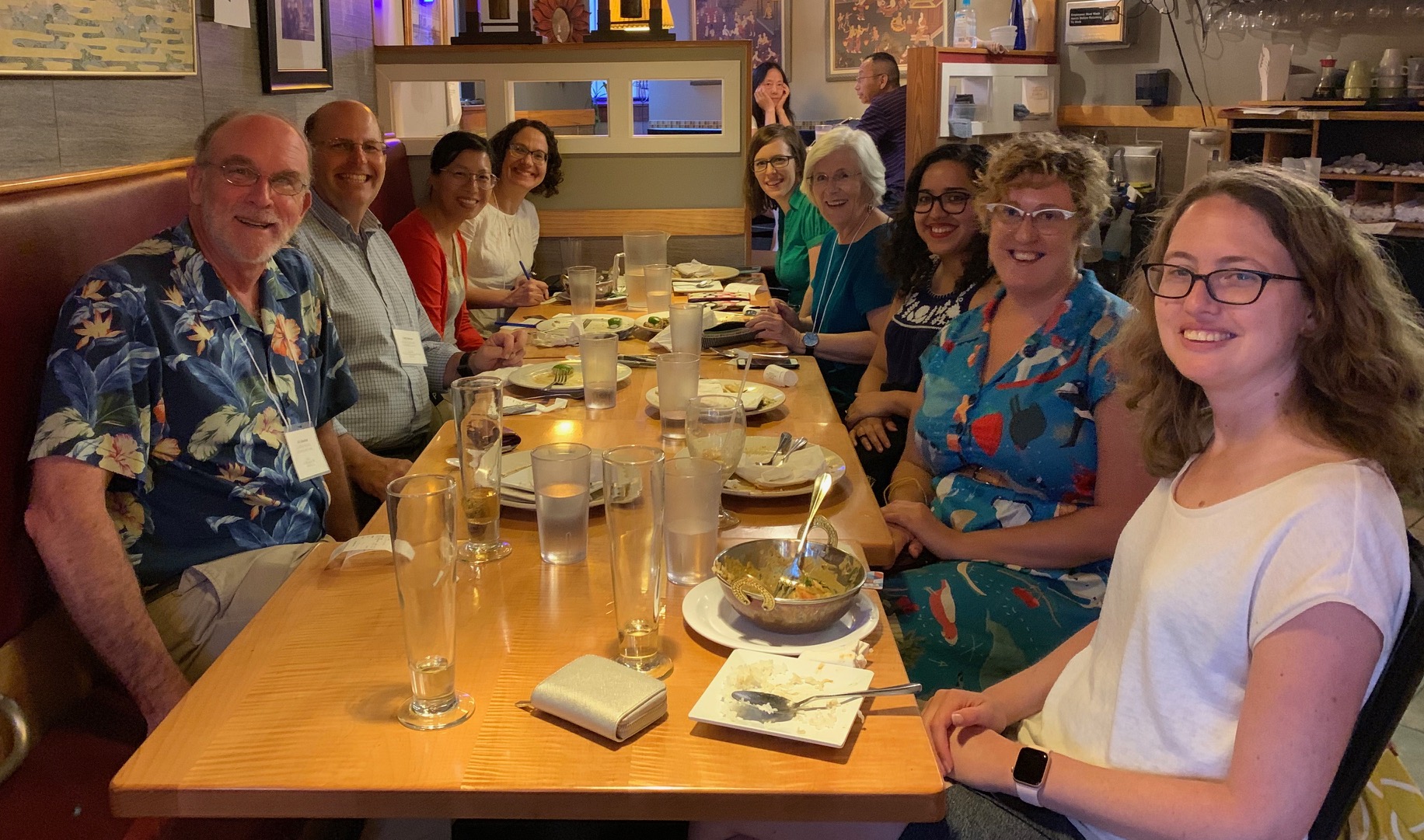






 For those new to RBS, things kick off Sunday afternoon, 5ish. There’s a reception, a Michael Suarez welcome speech & restaurant night. The latter an opportunity for ~ 10 students to share a meal at one of the local ‘Corner’ restaurants, in my case, Lemongrass Thai. Wonderful food, wonderful company!
For those new to RBS, things kick off Sunday afternoon, 5ish. There’s a reception, a Michael Suarez welcome speech & restaurant night. The latter an opportunity for ~ 10 students to share a meal at one of the local ‘Corner’ restaurants, in my case, Lemongrass Thai. Wonderful food, wonderful company!








 Eric Carle was born on June 25th, 1929 in Syracuse, New York, but his family originally being from Germany they moved back there and he was educated in art in Stuttgart. His father was drafted into the German army at the beginning of WWII, and eventually taken prisoner by Soviet Forces. Carle himself was also conscripted by the German government at the age of 15 to spend time with other boys his age building trenches on the Siegfried Line. Throughout all this time, Carle dreamed of returning to the United States, and finally, upon turning 23 he moved back to New York City with only $40 to his name. Carle was able to land a job as a graphic designer at
Eric Carle was born on June 25th, 1929 in Syracuse, New York, but his family originally being from Germany they moved back there and he was educated in art in Stuttgart. His father was drafted into the German army at the beginning of WWII, and eventually taken prisoner by Soviet Forces. Carle himself was also conscripted by the German government at the age of 15 to spend time with other boys his age building trenches on the Siegfried Line. Throughout all this time, Carle dreamed of returning to the United States, and finally, upon turning 23 he moved back to New York City with only $40 to his name. Carle was able to land a job as a graphic designer at  It was at this agency that author Bill Martin Jr. spotted a lobster Carle had drawn for an advert illustration and Martin decided to ask Carle to collaborate with him on a book for children – the result of which is one of Carle’s best known works… Brown Bear, Brown Bear, What Do You See? was published in 1967. The book was an immediate success for Martin (who authored the story) and Carle, and in relatively short time it became a best-seller. This popularity jump-started Carle’s career in books, and within just two years he was both writing and illustrating his own.
It was at this agency that author Bill Martin Jr. spotted a lobster Carle had drawn for an advert illustration and Martin decided to ask Carle to collaborate with him on a book for children – the result of which is one of Carle’s best known works… Brown Bear, Brown Bear, What Do You See? was published in 1967. The book was an immediate success for Martin (who authored the story) and Carle, and in relatively short time it became a best-seller. This popularity jump-started Carle’s career in books, and within just two years he was both writing and illustrating his own.


